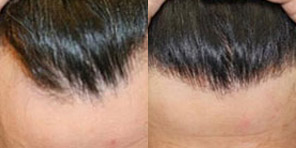
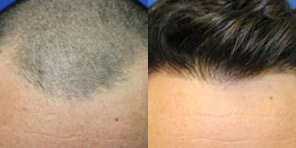
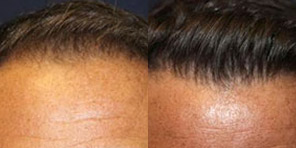
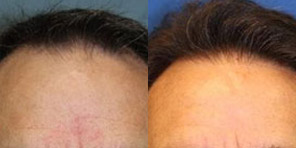
Frequently Asked Hair Restoration Questions

At California Hair MD, we make sure that our patients have all the information they need to make a confident decision about hair restoration.
Here are some of the most common questions that patients considering a hair restoration procedure have. To learn more about your options and the technology available, call (619) 633-3100 to schedule a personal consultation at our offices in San Diego, La Jolla, Newport Beach, or Beverly Hills.
Contents
- 0.1 What is the best form of hair replacement?
- 0.2 How much does it cost to replace your hair?
- 0.3 How much does ARTAS procedure cost?
- 0.4 Is ARTAS better than Neograft?
- 0.5 Does ARTAS hair transplant work?
- 0.6 Is ARTAS better than FUE?
- 0.7 How long does FUE last?
- 0.8 Is FUE better than FUT?
- 0.9 Does FUE really work?
- 0.10 Is FUE painful?
- 0.11 How long is recovery after FUE?
- 0.12 How long does FUT hair transplant last?
- 0.13 Which hair transplant is better FUT or FUE?
- 0.14 What does FUT mean in hair transplant?
- 0.15 Is FUT hair transplant worth it?
- 0.16 How long does hair restoration last?
- 0.17 What is the cost of hair restoration surgery?
- 0.18 Is it worth getting a hair transplant?
- 0.19 What is the best hair restoration?
- 1 Resources
What is the best form of hair replacement?
The best form of hair replacement surgery in 2022 is follicular unit extraction or FUE. The first hair restoration procedure was initially performed in 1952 by Dr. Norman Orentrich, a New York City dermatologist.(1) His technique was the forerunner of modern FUE methods but involved the use of large 4mm punches to harvest several follicular units at one time. His technique created a unnatural appearance to the patient’s hairline with a tufted or “doll’s hair” result. Modern FUE techniques initially described by a Japanese surgeon(2) in the early 20th century and refined by Bernstein(3) and others involve the use of a punch 1 mm or smaller in diameter that removes a single follicular unit in order to duplicate the way hair naturally grows in the human scalp.
Another method of hair replacement involves the use of a surgical scalpel to excise a large strip of scalp from the back of the head called follicular unit transplantation or FUT. While a large number of follicles could be removed at one session, patients often complained of a long recovery with pain, swelling, and numbness lasting weeks after surgery. A long, linear scar is created that may widen and require wearing a longer hair style to hide the appearance. (4,5)
How much does it cost to replace your hair?
The cost of hair replacement surgery depends upon several factors. Costs are based upon the extent of hair loss, type of technique or device, experience of the surgeon, and difficulty of the procedure. Hair loss confined to the frontal or crown area alone requires fewer grafts and is shorter in duration than if the hair loss involves multiple areas of the scalp. In general, strip surgery or FUT is less costly as it is a less sophisticated and more outdated technique than FUE requiring less skill and training for the surgeon and staff. FUE techniques are less invasive and result in less visible scars in most cases.
Difficult procedures can include revision or repeat hair restoration surgery and may be more expensive because they are more technically demanding. Hair restoration surgery costs also depend upon the experience and skill of the surgeon. In general, hair restoration costs vary from $10,000 to $25,000 based upon all of the above factors.
How much does ARTAS procedure cost?
The cost of the ARTAS procedure depends upon the degree of hair loss, experience and expertise of the surgeon and surgical team, and difficulty of the surgical procedure. The costs vary from $15,000 to $25,000.
Is ARTAS better than Neograft?
FAQ ARTAS VS NEOGRAFT Both the ARTAS and the Neograft are FUE or follicular unit extraction devices commonly used in hair restoration surgery. The ARTAS is the only robotic surgical device in the world. The punch that extracts hair follicles is housed in a 7-joint articulated robotic arm that is surrounded by stereoscopic cameras. These cameras constantly scan the surface of the scalp five times faster than the human eye. The cameras search out the most ideal follicles to harvest from the scalp. The ARTAS extracts follicles in a precise consistent and reproducible manner faster and more efficiently than a human. The surgeon controls the robotic harvesting from a user interface screen and can make minor adjustments to the angulation and depth of the punch to harvest the most ideal hair follicles. The ARTAS is designed for straight hair. It is not as efficient harvesting wavy or curly hair because of a higher transection rate of the hair follicles making them unsuitable for transplantation. Certain areas of the scalp may be difficult for the robotic arm to reach and harvest especially around the curvatures of the skull.
The ARTAS can also be used to make sites and place the hair follicles into the balding scalp in selected areas. The ARTAS cameras are able to visualize healthy existing hair follicles in the scalp and avoid damaging them during the transplantation process. A recent study reviewed the experience of 3 surgeons in 31 patients who underwent ARTAS robotic site making. The authors concluded there was no cosmetic difference in the patient outcomes between those who underwent site making by the ARTAS robot and those who underwent site making by a manual technique. However, site making robotically was significantly faster and consistent amongst three different surgeons. (6)
The newest version of the ARTAS is called the i-X-i. It allows for an even faster and more precise harvesting of hair follicles than earlier versions. Harvesting speeds of 1000 grafts or more per hour are quite common. Further upgrades and refinements to this system are done remotely to keep the system updated. Several studies have compared the transection rate of manual devices versus the ARTAS. Transected follicles are those which are damaged during harvesting and are not suitable for transplantation because they will not grow hair. In the original FDA clinical trials for the ARTAS robot, multi-center, prospective, blinded studies were conducted comparing manual FUE to robotic FUE. The average transection rate for harvesting follicles by hand was 26% versus 8% when the follicles were harvested robotically with the ARTAS.(7)
Neograft is a semi automatic device also designed for FUE. The operator uses a hand piece that contains a small sharp surgical punch to extract hair follicles from the donor region. Once the grafts are harvested they are gently suctioned into a reservoir filled with saline. It is an FUE device that is applicable to all hair types both straight and curly. Neograft can also be used to make recipient sites in the balding scalp and insert grafts. However, most physicians prefer making the recipient sites by hand and manually inserting the grafts one by one. Neograft is one of the most popular and commonly used FUE devices in the USA today.
Many surgeons will combine the devices during the harvesting and transplantation process. The Neograft device can be used to harvest some grafts which the ARTAS robotic arm cannot reach. This hybrid approach allows the surgeon to use the advantages of robotic technology where applicable and still maximally harvest the donor area with the Neograft device.
While there are specific advantages and indications to these two FUE devices, what matters most is the physician who chooses the device and operates it. It is the surgical experience and training which determine the final outcome as much as the actual FUE device.
Does ARTAS hair transplant work?
ARTAS hair transplantation is the most advanced FUE hair restoration device available today. While it is FDA approved for black straight hair(8), surgeons can temporarily dye the hair of patients with light or white hair so that the robotic cameras can recognized the hair follicles for harvesting. Patients with lightly wavy hair may also be robotic hair restoration candidates. The ARTAS i-X uses a digital and visually guided punch to harvest hair follicles using a 2 step punch technique. The ARTAS i-X provides superior accuracy, precision, speed, consistency, and predictability as compared to other manual and semi-automatic FUE devices on the market. It has a precision of less than 1 mm. Finally, the hair restoration surgeon has much less fatigue when using the ARTAS robot than older FUE methods. The ARTAS i-X can also make sites in the frontal area and transplant hair follicles robotically.
Is ARTAS better than FUE?
The ARTAS i-X-i robot is a follicular unit extraction (FUE) method of hair transplantation. Many surgeons feel that it is the best FUE method available today in the right type of patient because of its accuracy, speed, and consistency in creating intact follicular units. The ARTAS i-X-I is also capable of making sites in the balding scalp for transplanting new hair follicles without damaging surrounding normal hair follicles by avoiding existing healthy hair follicles more accurately than the human eye is capable of doing.
It is well known that manual FUE procedures can be lengthy and time consuming for the surgeon creating fatigue as well as pain and discomfort. When this happens, it is possible that this results in human error with higher damage and transection of hair follicles during the harvesting process and a lower yield of healthy hair follicles for transplantation. (9,10)
Manual FUE means that there is more manipulation of the hair follicles. This can result in a higher risk of damage to the hair follicle which can reduce survivability and growth following transplantation. (11)
How long does FUE last?
Follicular unit extraction (FUE) is a permanent solution to hair loss for both men and women provided the hair follicles that are harvested from the donor areas are within the “safe zone”. The safe zone is an anatomic region of the scalp located along the back (occipital) area that will not undergo alopecia in the future. Dr. Norman Orentrich, a New York Dermatologist, established in 1994 that this safe zone was based upon his examination of 328 men over the age of 65. He found that 80% of patients under age 80 years of age would retain their hair within these boundaries in their lifetime. When these hair follicles were transplanted from the “safe zone” they were expected to grow throughout the patient’s lifetime. (12)
Is FUE better than FUT?
There are a number of distinct advantages of FUE over FUT hair restoration. FUE is a less invasive procedure than FUT resulting in less postoperative pain, swelling, and scalp numbness because it is a more superficial procedure. There is less damage to cutaneous sensory nerves with FUE versus FUT. FUE avoids a long, linear scar which may widen with time and reduce the amount donor hair follicles available for a future transplantation procedure if needed. The scar from an FUT procedure may also necessitate a longer hair style to camouflage the donor scar. It is also possible to obtain as many hair follicles from the donor area over time with FUE as with FUT. If a patient desires to reduce the appearance of donor scar from an FUT then an FUE procedure will be necessary. However, the donor follicles available for future hair transplantation may be reduced as they are used to correct the long linear scar from an FUT procedure.
In 2006, 91% of hair transplant procedures were FUT and only 9% were FUE methods. However, in only 10 years 55% of hair transplant procedures were FUE and 45% were FUT methods. In 2022, the majority of hair restoration procedures are done using FUE techniques.
Does FUE really work?
Yes, FUE does really work. FUE is now the most frequently performed method of hair restoration performed in the USA. It is considered the “gold standard” for hair transplant surgery, and the most frequently requested method by most men and women who are considering hair restoration surgery.
Is FUE painful?
There is some postoperative pain with any hair restoration procedure, including FUE. However, many patients who undergo FUE have previously undergone FUT. These patients consistently describe significantly less pain, swelling, numbness, and shorter recovery times after undergoing FUE as compared to FUT surgery. Most FUE patients only use pain medication on the day of the procedure and are able to use acetaminophen on the next few days after hair replacement surgery to manage their pain.
How long is recovery after FUE?
The recovery following FUE is significantly less than with FUT. Healing in the donor area occurs within 10-14 days with hairs growing in the donor region obscuring and covering the donor harvesting sites. In the transplanted areas, small scabs or crusts occur where the grafts are placed but usually fall off within 7-10 days after surgery. In contrast, healing in the donor area is significantly longer and more painful in patients who undergo FUT versus FUE with a greater need for oral narcotics, more swelling, and numbness that may last weeks to months in duration.
How long does FUT hair transplant last?
The results of FUT are as long lasting as with FUE when the grafts are taken from the “safe zone” along the back and sides of the scalp. However, many surgeons feel that the graft quality from FUT is more dependent upon the surgical team that manipulates and divides the strip of scalp into individual follicles which are to be transplanted into areas of hair loss than is the case with FUE cases where there is much less manipulation of follicles and potentially less trauma and damage to them.
Which hair transplant is better FUT or FUE?
Most hair restoration practices that perform both FUT and FUE hair transplantation surgery feel that the final aesthetic (cosmetic) result to correct hair loss is similar when comparing these two techniques. However, the scar in the donor area is more likely to be noticeable with FUT since it is a long linear scar, something the eye can easily see and follow. Basic plastic surgical principles dictate that smaller, irregular scars like those obtained from FUE are much more difficult to see than long linear straight scars from FUT.
What does FUT mean in hair transplant?
FUT stands for follicular unit transplantation and is commonly referred to as “strip surgery” because it involves removing a strip of scalp from the back and sides of the scalp.
Is FUT hair transplant worth it?
Most patients who have undergone FUT hair transplantation surgery are satisfied with the improvement in their hair loss. However, many patients who underwent FUT were unaware of FUE and regret not having undergone the newer FUE method for hair transplantation. When previous FUT patients decide to undergo additional hair restoration surgery, most of them choose FUE.
How long does hair restoration last?
Hair loss in both men and women is both progressive and permanent in nature. However, the results of well designed and well executed hair restoration surgery can last a lifetime and be permanent if the follicles which the surgeon removes and transplants are taken from areas of the scalp along the back and sides of the scalp. It is these areas of the scalp which are genetically resistant to balding and allow the surgeon to transplant these hair follicles into the regions where hair loss has already occurred.
However, if the hair follicles are taken from areas of the scalp along the back and sides of the scalp which are too close to the top of the head or crown region then these transplanted hair follicles may stop producing hair at some time in the years ahead as the patient’s hair loss progresses.
Hair transplant surgery involves the removal of hair follicles from the back and sides of the head which are then transplanted into the areas in the scalp which are balding. These include the frontal area, midscalp, and crown regions which have undergone androgenic alopecia or male pattern baldness. While it is assumed these transplanted hair follicles will survive indefinitely, there is very little in the scientific literature that supports this claim. However, a recent article in the Journal of Cutaneous and Aesthetic Surgery attempted to answer this question. This study looked at the longevity of hair follicles that were obtained by follicular unit transplantation (FUT) in 112 patients over a 4 year period of time.(13)
These authors looked at the longevity of hair follicles in this group of patients comparing the results of hair transplantation at 1 year versus 4 years. Of the 112 patients which were studied, half of the patients had grade 4 hair loss, 46% were grade 5, and 3% had grade 6 alopecia. At 4 years following hair transplantation, 55% of their patients demonstrated moderate reduction in density at 4 years vs 1 year, 28% had slightly reduced density, 8% had greatly reduced density, and 9% demonstrated no change in their density.
The authors did not indicate what method(s) were used to determine the final percentage density in their patients as the results quoted may not be an accurate assessment of density if just based upon visual observation of each patient’s scalp versus the use of an analytic measurement device. Also, it is unclear how many of these patients were on medical therapy for hair loss. Finally, the longevity of the transplanted follicles may have been affected by the quality of the transplant team performing the initial transplant procedure especially if the hair follicles were damaged at the time of transplant surgery.
Nevertheless, it is an interesting study. More such studies are needed to answer the question as to how long hair restoration lasts. Future studies will need larger series of patients and more accurate methods to determine that patient’s post-transplantation density. Other factors including the type of transplantation method (FUE vs FUT), the use of medical therapy to prevent further hair loss, the anatomic structure of the patient’s hair follicles (coarse vs fine, straight vs curly), and the status of the balding scalp at the time of transplantation need to be addressed as well. Finally, and most importantly, the results of hair restoration surgery vary and are directly dependent upon the expertise of the surgical team involved in the procedure.
What is the cost of hair restoration surgery?
The cost of hair restoration depends upon many factors and can vary in costs from $7000 – $20,000. (14)(15) These procedures are not covered by health insurance plans. In general, the cost of this procedure is based upon the following factors:
• Degree of baldness
• Prior history of hair transplant surgery
• Repair or reconstruction of prior failed hair transplant surgery
• Status of the donor area(s)
• Experience and expertise of the surgeon
• Medical device for hair transplantation
• Geographic region of the country
As expected, the greater the amount of baldness then the greater the total cost for the procedure. Larger areas of baldness will require transplanting a larger number of hair follicles or grafts from the donor area(s). This makes the procedure longer in duration and more complex.
Patients who have undergone prior hair transplant surgery may wish to improve the results of the previous procedure by having more density in the area that was transplanted or correct baldness in a different region of the scalp. In some cases, the cosmetic results of a previous hair transplant were less than ideal. Repair or reconstruction of previous hair transplant surgery can be challenging and complicated.
The status of the donor area is important as it can be compromised by previous harvesting and scars limiting the amount of hair follicles that can be successfully removed for transplantation. This is why the experience and expertise of the surgeon matter as it will have an impact on the final cosmetic outcome.
There are numerous surgical techniques and devices that can be employed for successful hair restoration surgery. Some of the devices available today are more costly because of the expenses associated with their use. Finally, the costs of hair restoration vary depending upon the region of the country. Costs are higher in large metropolitan areas where the cost of living is higher.
Is it worth getting a hair transplant?
Hair loss affects millions of men and women in the United States. On average, 40% of men will suffer hair loss in their 40’s, 50% in their 50’s, and nearly 2/3rds in their 60’s. Hair loss can result in significant emotional distress, affect a patient’s self confidence and negatively impact their self image. 94% of patients who had undergone hair transplant surgery indicated that they felt the procedure was worth it on a recent Real Self survey online.
What is the best hair restoration?
The two primary types of hair restoration are follicular unit transplantation (FUT) or the so called “strip procedure” and follicular unit extraction (FUE). In 2006, the majority of hair restoration procedures were performed using the FUT method. However, by 2016 most hair restoration procedures were performed using the FUE method. Today, most hair restoration procedures in the USA are done using FUE as the preferred method. (4) FUE is now considered the gold standard in hair restoration because it is less invasive than FUT with less discomfort, swelling, and scarring in the donor area. There is good clinical evidence that graft quality obtained by FUE is equivalent to graft quality obtained by FUT.(16)
With the development of the Artas robotic FUE system, the harvesting process is accomplished robotically with the oversight by the physician. It appears that robotic FUE results in a lower transection rate than manual devices because of the built in artificial intelligence (AI) in the system and the computer cameras scanning of the scalp to find the best hair follicles for harvesting.
In a recent study that evaluated the robot’s ability to accurately harvest intact hair follicles suitable for transplantation, the authors discovered that the Artas robot successfully harvested 95% of all hair follicles with no damage.(17) This is in contrast to manual FUE devices which quote lower rates of harvesting intact hair follicles.
Resources
- Choudhry N, Sood A, Steinweg S. Norman Orentreich, The Father of Hair Transplantation. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153(8):837. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2017.2097
- Inaba, M., Inaba, Y. (1996). Therapy for Androgenetic Alopecia. In: Androgenetic Alopecia. Springer, Tokyo. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-4-431-67038-4_25
- Rassman WR, Bernstein RM, McClellan R, Jones R, Worton E, Uyttendaele H. Follicular unit extraction: minimally invasive surgery for hair transplantation. Dermatol Surg. 2002;28(8):720-728. doi:10.1046/j.1524-4725.2002.01320.x
- Bicknell LM, Kash N, Kavouspour C, Rashid RM. Follicular unit extraction hair transplant harvest: a review of current recommendations and future considerations. Dermatology Online Journal. 2014;20(3). doi:10.5070/D3203021754
- Wesley CK, Unger RH, Rosenberg M, Unger MA, Unger WP. Factors influencing postoperative hyperesthesia in hair restoration surgery. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2011;10(4):301-306. doi:10.1111/j.1473-2165.2011.00582.x
- Kanayama, Koji MD, PhD*,†; Kato, Harunosuke MD, PhD*; Mori, Masanori MD*; Sakae, Yuki MD*; Okazaki, Mutsumi MD, PhD†. Robotically Assisted Recipient Site Preparation in Hair Restoration Surgery: Surgical Safety and Clinical Outcomes in 31 Consecutive Patients. Dermatologic Surgery 47(10):p 1365-1370, October 2021. | DOI: 10.1097/DSS.0000000000003152
- Berman, David A. New Computer Assisted System May Change the Hair Restoration Field. Practical Dermatology. September 2011, 32-35. http://v2.practicaldermatology.com/pdfs/PD0911_Fea_HairRestoration.pdf
- Dua A, Dua K. Follicular unit extraction hair transplant. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2010;3(2):76-81. doi:10.4103/0974-2077.69015
- Williams KL Jr, Gupta AK, Schultz H. Ergonomics in hair restoration surgeons. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2016;15(1):66-71. doi:10.1111/jocd.12188
- Avram MR, Watkins SA. Robotic follicular unit extraction in hair transplantation. Dermatol Surg. 2014;40(12):1319-1327. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000000191.
- Garg AK, Garg S. Donor Harvesting: Follicular Unit Excision. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2018;11(4):195-201. doi:10.4103/JCAS.JCAS_123_18
- Unger W, Solish N, Giguere D, et al. Delineating the “Safe” Donor Area for Hair Transplanting. The American Journal of Cosmetic Surgery. 1994;11(4):239-243. doi:10.1177/074880689401100402
- Kumaresan M, Subburathinam DM. Longevity of Hair Follicles after Follicular Unit Transplant Surgery. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2020;13(4):292-297. doi:10.4103/JCAS.JCAS_44_20
- Dunkin MA. Hair Transplant Procedures: Average Cost, What to Expect, and More. WebMD. Published April 26, 2022. https://www.webmd.com/skin-problems-and-treatments/hair-loss/hair-transplants
- Gotter A, Sherrell Z. How Much Does a Hair Transplant Cost? Healthline. Published June 29, 2022. Accessed November 17, 2022. https://www.healthline.com/health/cost-of-hair-transplant#bottom-line
- Gupta AK, Quinlan EM. Changing trends in surgical hair restoration: Use of Google Trends and the ISHRS practice census survey. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology. 2020;19(11):2974-2981. doi:10.1111/jocd.13723
- Gupta, Aditya K. MD, PhD, FRCPC*,†; Love, Robin P. MSc†; Harris, James A. MD, FACS‡. Old Friend or New Ally: A Comparison of Follicular Unit Transplantation and Follicular Unit Excision Methods in Hair Transplantation. Dermatologic Surgery: August 2020 – Volume 46 – Issue 8 – p 1078-1083 doi: 10.1097/DSS.0000000000002373